Global S&T Development Trend Analysis Platform of Resources and Environment
| Implantable gold sensor can help monitor vital values, drug effectiveness | |
| admin | |
| 2021-04-12 | |
| 发布年 | 2021 |
| 语种 | 英语 |
| 国家 | 国际 |
| 领域 | 地球科学 |
| 正文(英文) |  Gold nanoparticles. (Image by Veronika Sapozhnikova, Konstantin Sokolov, Rebecca Richards-Kortum, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center; Rice University-National Institutes of Health, Flickr).
Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz have developed an implantable sensor based on color-stable gold nanoparticles. The sensor can be operated in the body for several months. Embedded into an artificial polymeric tissue, the nanogold is implanted under the skin and it changes its color to report information on vital values and concentrations of substances or drugs. Up until now, implantable sensors have not been suitable to remain in the body permanently because either the body rejects them or because the sensor’s color is unstable and fades over time.
However, by using gold nanoparticles, the team at JGU achieved a more stable device. In a study published in the journal Nano Letters, the researchers explain that gold nanoparticles act like small antennas for light: They strongly absorb and scatter it and, therefore, appear colorful. They react to alterations in their surrounding by changing color. The way it works is that the nanoparticles are embedded in a porous hydrogel with a tissue-like consistency. Once implanted under the skin, small blood vessels and cells grow into the pores. The sensor is then integrated into the tissue and is not rejected as a foreign body. “Our sensor is like an invisible tattoo, not much bigger than a penny and thinner than one millimeter,” Carsten Sönnichsen, co-author of the study, said in a media statement. The gold nanoparticles are infrared so they are not visible to the eye. Yet, a special kind of measurement device can detect their color non-invasively through the skin. 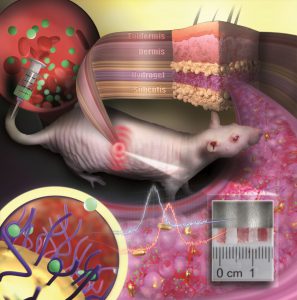 To test their invention, the group implanted their gold nanoparticle sensors under the skin of hairless rats. Color changes in these sensors were monitored following the administration of various doses of an antibiotic. As drug molecules got into the sensor via the bloodstream, they bound to specific receptors on the surface of the gold nanoparticles and induced color change that is dependent on drug concentration. Thanks to the color-stable gold nanoparticles and the tissue-integrating hydrogel, the sensor was found to remain mechanically and optically stable over several months. “We are used to colored objects bleaching over time. Gold nanoparticles, however, do not bleach but keep their color permanently. As they can be easily coated with various different receptors, they are an ideal platform for implantable sensors,” Katharina Kaefer, first author of the paper, said. According to Kaefer, this concept is generalizable and has the potential to extend the lifetime of implantable sensors. In her view, gold nanoparticle-based implantable sensors could be used to observe concentrations of different biomarkers or drugs in the body simultaneously. Such sensors could find application in drug development, medical research, or personalized medicine, such as the management of chronic diseases.
|
| URL | 查看原文 |
| 来源平台 | Minging.com |
| 文献类型 | 新闻 |
| 条目标识符 | http://119.78.100.173/C666/handle/2XK7JSWQ/322161 |
| 专题 | 地球科学 |
| 推荐引用方式 GB/T 7714 | admin. Implantable gold sensor can help monitor vital values, drug effectiveness. 2021. |
| 条目包含的文件 | 条目无相关文件。 | |||||
| 个性服务 |
| 推荐该条目 |
| 保存到收藏夹 |
| 查看访问统计 |
| 导出为Endnote文件 |
| 谷歌学术 |
| 谷歌学术中相似的文章 |
| [admin]的文章 |
| 百度学术 |
| 百度学术中相似的文章 |
| [admin]的文章 |
| 必应学术 |
| 必应学术中相似的文章 |
| [admin]的文章 |
| 相关权益政策 |
| 暂无数据 |
| 收藏/分享 |
除非特别说明,本系统中所有内容都受版权保护,并保留所有权利。
修改评论