
Global S&T Development Trend Analysis Platform of Resources and Environment
| How to stop the next pandemic | |
| admin | |
| 2020-04-27 | |
| 发布年 | 2020 |
| 语种 | 英语 |
| 国家 | 美国 |
| 领域 | 资源环境 |
| 正文(英文) |
In the midst of this pandemic, we are all rightly focused on what we can do to protect ourselves and each other, and on how we can slow or stop the spread of the virus that causes Covid-19. But I want to take a moment to look ahead. I want to ask what we know that could help prevent future pandemics. The answer might surprise you.Over the past 50 years, humans have been exposed to hundreds of emerging infectious diseases. About 75% of these emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic – diseases that can be transmitted between humans and other animals like mammals, birds, and reptiles. Covid-19 is a zoonotic disease. We think it jumped to us from a wild mammal, and then began spreading between people. We also know that we can transmit the virus to other species, like tigers, lions, and Syrian hamsters [1]. You’re familiar with other zoonotic diseases, too. Lyme disease is zoonotic, and so is Ebola. SARS and MERS are zoonotic, and far back in human history, tuberculosis, smallpox, and the plague also emerged from animals.  If animals are the sources of so many infectious diseases, should we be afraid of wildlife? Is biodiversity dangerous? This would be true if all kinds of animals were equally likely to transmit pathogens to us. If that were true, the more types of animals there are, the greater the risk would be. But they’re not equally likely. In fact, the next zoonotic disease is far more likely to come from a rat than a rhino. It’s worth learning why. Most zoonotic diseases come from mammals, our closest relatives [2]. There are lots of different kinds of mammals, from aardvarks to elephants to leopard seals. But the most diverse mammals – by far – are the rodents [3]. Perhaps not surprisingly, then, most zoonotic viruses have come from rodents. Rodents are remarkable creatures, and many of them are quite resilient, even to the kinds of damage that we’re doing to the environment. A recent study found that 100% of some Orders [4] of mammals are threatened. Which ones? Rhinos and their relatives. Manatees. Bandicoots [5]. Primates aren’t doing so well either. How are rodents doing? Few are threatened. Rodents are less vulnerable to biodiversity loss than other types of mammals are.  But even within the rodents, some species harbor many more dangerous pathogens than others do. What do we know about the rodents that harbor these pathogens? And how are they different from the rodents that don’t? For this question, I’ll turn to the work of Barbara Han, a Red Hook resident, dear friend, and scientist at the Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies in Millbrook. She and her colleagues found that rodents that have given us zoonotic pathogens have certain traits in common. They tend to have large geographic ranges and short lifespans. They tend to mature early in their short lives, and to have lots of babies in each litter [6]. These are the very traits of species that thrive when people disturb and disrupt ecosystems. Many years ago, my own work in Kenya revealed a pattern that is now widely documented: when biodiversity is lost, rodents thrive. In African savannas, for example, elephants, giraffes, and zebras dominate when biodiversity is high. But when these charismatic large species disappear – and they are always the losers in a competition with people – rodents become twice as abundant.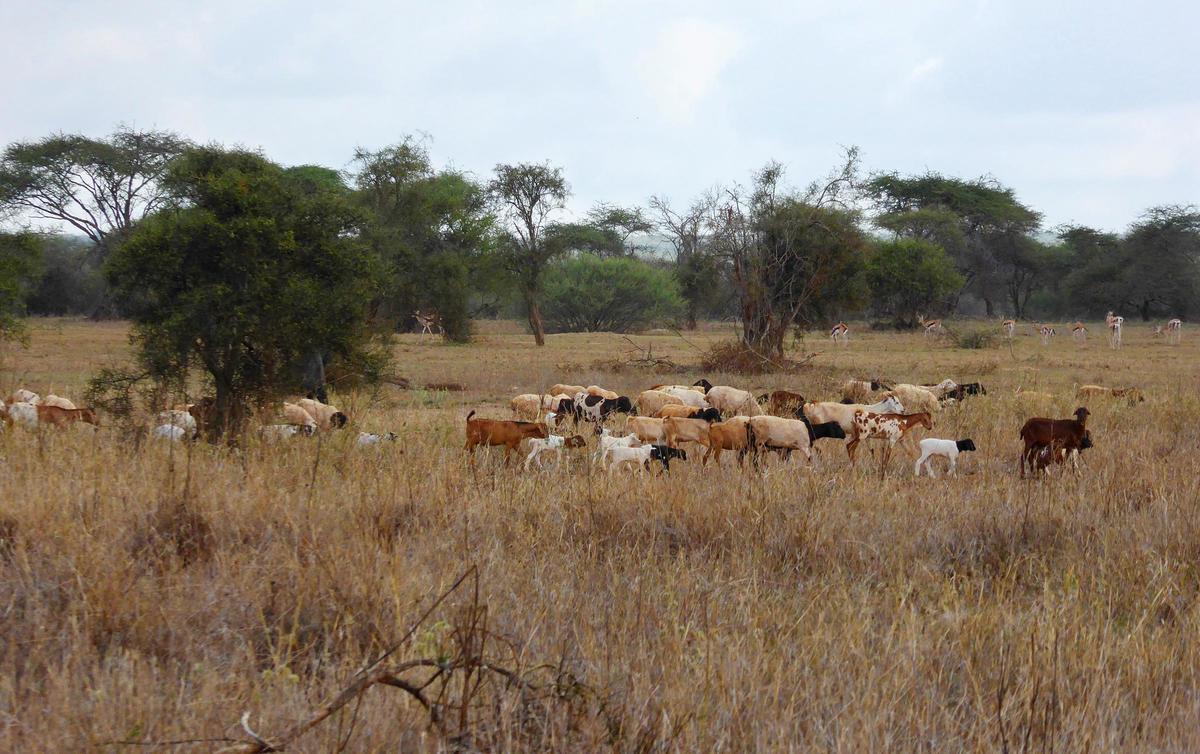  Closer to home, Rick Ostfeld and I, together with our colleagues, have shown that biodiversity also keeps rodent abundance low in northeastern forests of the United States. This has huge consequences for our health because when rodent abundance is high, our risk of contracting Lyme disease and other tick-borne diseases skyrockets. For Lyme disease, as for so many emerging infectious diseases, rodents are the most common source of the zoonotic pathogen that makes us sick. Biodiversity is not bad for us. Indeed, biodiversity actually protects our health. That’s because areas with high biodiversity have lower densities of the species most likely to make us sick. There is much we can learn from the current global catastrophe that will help us contend better with future epidemics. But it would be far better if we could prevent future epidemics altogether. One of the best ways to do that is to preserve, protect, and restore natural biodiversity. Notes
|
| URL | 查看原文 |
| 来源平台 | Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies |
| 文献类型 | 新闻 |
| 条目标识符 | http://119.78.100.173/C666/handle/2XK7JSWQ/273691 |
| 专题 | 资源环境科学 |
| 推荐引用方式 GB/T 7714 | admin. How to stop the next pandemic. 2020. |
| 条目包含的文件 | 条目无相关文件。 | |||||
| 个性服务 |
| 推荐该条目 |
| 保存到收藏夹 |
| 查看访问统计 |
| 导出为Endnote文件 |
| 谷歌学术 |
| 谷歌学术中相似的文章 |
| [admin]的文章 |
| 百度学术 |
| 百度学术中相似的文章 |
| [admin]的文章 |
| 必应学术 |
| 必应学术中相似的文章 |
| [admin]的文章 |
| 相关权益政策 |
| 暂无数据 |
| 收藏/分享 |
除非特别说明,本系统中所有内容都受版权保护,并保留所有权利。
修改评论